Mouse Arm
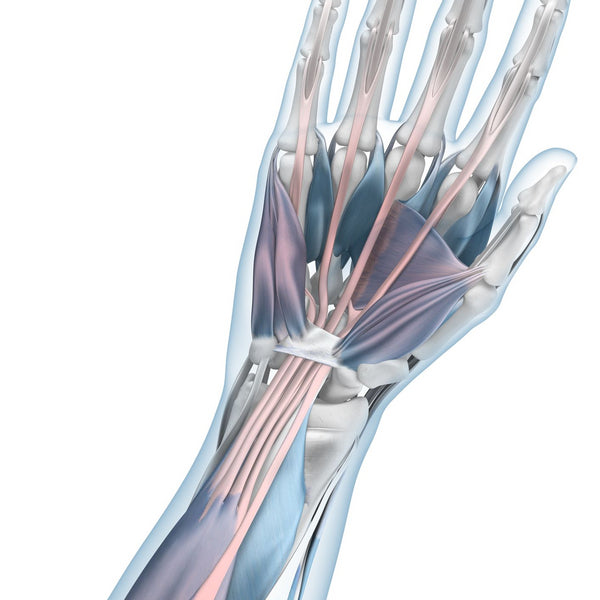
Mouse Arm: Muscles and Tendons in the Arm Degeneration

Our hands are complex structures made of bone, joints, muscles and tendons. Together they facilitate the transfer of power to the hand and the palm allowing for stretching and bending the hand.
Overloading of the connective tissue and the tendons from using a computer or mouse for prolonged periods of time can lead to developing pain and discomfort. Milder cases often ease over time, however the underlying condition persists.
Over time these tiny injuries called micro-traumas accumulate and can lead to a degeneration of certain muscles and tendons in the arm. This is known as “Mouse Arm” or "Mouse Arm Syndrome".
Chronic cases can lead to severe complications and irreversible damage. With early diagnosis and treatment being the best chance to prevent long term damage and facilitate a speedy recovery.
Causes of Mouse Arm Syndrome

Broadly speaking “mouse arm” can be traced to three main risk factors. These are:
- Micro-traumas: Micro-traumas are small injuries in the tendons and connective tissues of the hand. These injuries result from a combination of unhealthy proprioception and repetitious movements of the hands. For example, it is common for people working long hours on a computer to overstress their hands working on a keyboard and mouse, accumulating micro-traumas over time.
- A lack of ergonomics in the workplace often leads to repetitive strain injury syndrome (RSI). Poor quality of infrastructure such as desks and chairs, or poor use of equipment like tables and mouse pads (quality and fit) can lead to overstressing the hands. For example, uncomfortable chairs or tables (specifically height of the table) are fairly common stressors that commonly lead to such a condition.
- Accidental trauma or injury can lead to damage to the tendons and connective tissue.
Mouse Arm Syndrome Symptoms
Some of the more common symptoms of the mouse arm include:
- Increased muscle tension in the hands. This causes stiffness and can lead to pain in the hands when under stress or undertaking an activity.
- Pain and a tingling sensation in the hand often result from overloading the hand. The patient can experience swelling and stiffness as a result.
- There is a reduced supply of oxygen and nutrients to the cells that leads to weakness and increased localised swelling.
- In severe cases, chronification occurs. This causes the brain to associate activities with pain. A patient develops phantom pain in the hand, and it is persistent. There is significant discomfort and the mobility is severely restricted. This means even in the right position you can still suffer from the condition.
Long term neglect of “Mouse arm” can lead to serious irreversible consequences. An early diagnosis is in the patient’s best interest.
Diagnosis of Mouse Arm Syndrome
A medical professional (usually a GP or Physiotherapist) begins with a complete patient history and thorough physical examination of the elbow. This provides critical information about the risk factors to the patient as well as allows for a study of the progression of the condition.
Sophisticated imaging technology like X-Rays and ultrasound can be used to get more information about the condition of the bones, muscles and tendons in the joint.
Treatment for Mouse Arm Syndrome
Treatment for Mouse Arm is mostly conservative. Proving ample support and stabilization to the joint can help control the damage done to the wrist. Early intervention is the best course of action to prevent degeneration and permanent nerve damage.
-
Ergonomic Redesign of Workplace
One of the most efficient preventative measures against mouse arm would be to work with your employer to redesign the office furniture with well-being in mind. Comfortable chairs and adjustable tables are good examples of a simple measure that can be taken in everyday work life.
-
Ergonomic Mouse Armrest
If using a computer and mouse are necessary at work, using a comfortable and proper sized mouse with a mouse pad can significantly reduce the risk of mouse arm.
-
Immobilisation
Immobilising the forearm temporarily has proven effective to manage the symptoms of the condition, best done with a medical brace. This allows the wrist to rest and heal quicker.
-
Rehabilitation, Physiotherapy And Occupational Therapy
Regular Physical therapy helps with targeted muscle training and is a proven effective treatment path. The physiotherapy exercises can help promote the reorganisation of the muscles and are the most effective option to curb the disease. Encouraging healthy proprioception and strengthening of the muscles in the wrist helps prevent long term degeneration.
Regular targeted exercises can help maintain the mobility and effective functioning of the joint and is highly recommended. Progressive muscle relaxation exercises (PMR) can be effective to stretch the muscles and help them relax, and these can be shown by most medical professionals.

-
Prescribed Painkillers
Painkillers such as Ibuprofen or Panadol can be used to help alleviate pain and discomfort in patients, but should only be used when directed by a medical professional. Pain, however, is a crucial indicator of the injury.
Painkillers merely mask the pain without addressing the underlying condition. Long term use of painkillers has negative side-effects and can be counter-productive.
-
Medical Wrist Brace
Medical wrist braces/splints help to reduce the pain and discomfort patients experience by relieving the joint.
Wearing a Bauerfeind wrist brace like the ManuLoc or ManuTrain helps to greatly minimise the chances of injury by providing enhanced stability, proprioception and medical-grade compression.
This is not found in simple neoprene sleeves and braces and can be instrumental in a speedy recovery.
Mouse Arm Syndrome Sleeves & Braces

Medical braces like the ManuLoc and ManuTrain often prove highly effective in managing the symptoms of mouse arm and preventing its progression. The brace provides compression and anatomical fit to speed up recovery.
This encourages healthy proprioception and provides stability to the wrist and can be worn comfortably through physiotherapy. With regular use patients experience relief from their symptoms much quicker, and have a greatly improved quality of life.
The ManuTrain is a compression sleeve that targets the areas most commonly inflamed with inbuilt gel supports that reduce swelling and inflammation, and massage the area constantly to relieve pain. An adjustable strap and removable stay make this ideal for milder cases, whether you’re at home, at work or playing sports.
The ManuLoc is a rigid splint that is anatomically contoured, and can be shaped to each person’s wrist to give the best support possible. With an adjustable strapping system, lightweight build and freedom of movement for the fingers and thumb, it’s ideal for moderate to severe cases and great for all-day wear.
For assistance selecting the right product for your needs, book a video consultation with a Bauerfeind expert: Book Video Call, or call us on 1300 668 466.
Do you have private health? Most private health extras will cover Bauerfeind Products, check to see if yours is included. Bauerfeind Private Health Insurance Inquiry.
Bauerfeind products are developed at our innovation and manufacturing facility in Zeulenroda, Germany. Based on years of scientific research, our award-winning braces and support garments are highly recommended by medical professionals and athletes worldwide.




